Difference between revisions of "Basic lua: Operators"
From The Official Visionaire Studio: Adventure Game Engine Wiki
| Line 229: | Line 229: | ||
{| class="ts" | {| class="ts" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | <big>+</big> || width="90%" | Add |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | <big>-</big> || Subtract or invert |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | <big>*</big> || Multiply |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | <big>/</big> || Divide |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | <big>^</big> || Power |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | <big>%</big> || Remainder |
|} | |} | ||
{{toc}} | {{toc}} | ||
Revision as of 12:27, 21 August 2014
Lua operators are expressions used to perform calculations or to pass arguments between different value types.
Conditional Operators
| if | Query if something does or does not meet a certain condition. |
| else | Do something else if the query condition was not met. |
| elseif | Used to add additional if queries, if the initial query condition was not met. |
| end | This is used to close various queries or functions; there must be the same amount of end as if; except in instances where elseif has been used. |
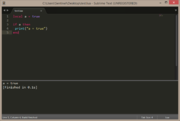
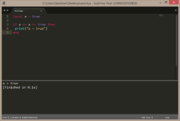
| Example 1: if condition is true (method 1) | |
|---|---|
local a = true
if a then
print("a = true")
end |
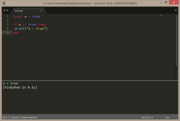
| Example 2: if condition is true (method 2) | |
|---|---|
local a = true
if a == true then
print("a = true")
end |
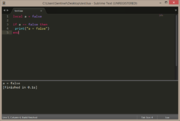
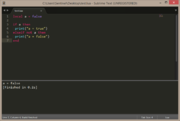
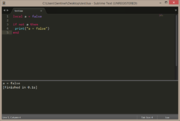
| Example 3: if condition is false | |
|---|---|
local a = false
if a == false then
print("a = false")
end |
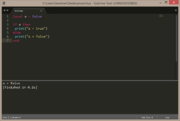
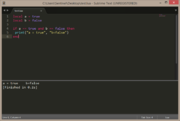
| Example 4: if condition is not met, then do else | |
|---|---|
local a = false
if a then
print("a = true")
else
print("a = false")
end |
| Example 5: if condition is not met, then do elseif | |
|---|---|
local a = false
if a then
print("a = true")
elseif not a then
print("a = false")
end |
Logical Operators
| and | Allows you to check multiple conditions in a single if query. |
| or | Allows you to add an alternative if query into a single if query. |
| not | Checks if condition equals false or negative. |
| Example 1: if condition a is true and condition b is false then | |
|---|---|
local a = true
local b = false
if a == true and b == false then
print("a = true", "b=false")
end |
| Example 2: if condition is true or condition == true then | |
|---|---|
local a = true
if a or a == true then
print("a = true")
end |
| Example 3: if condition is not true | |
|---|---|
local a = false
if not a then
print("a = false")
end |
Comparison Operators
| == | Equal to. |
| ~= | Does not equal. |
| >= | Greater than or equal to. |
| > | Greater than. |
| <= | Less than or equal to. |
| < | Less than. |
| Example 1: if a equals 1 | |
|---|---|
local a = 1
if a == 1 then
print("a = 1")
end |
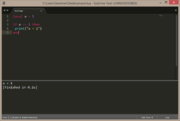
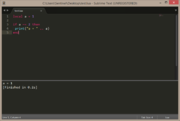
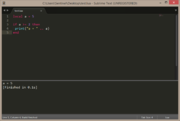
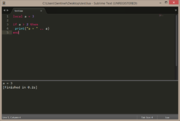
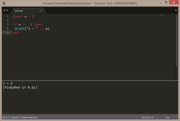
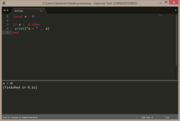
| Example 2: if a does not equal 2 | |
|---|---|
local a = 1
if a ~= 2 then
print("a = " .. a)
end |
| Example 3: if a is greater than or equal to 2 | |
|---|---|
local a = 5
if a >= 2 then
print("a = " .. a)
end |
| Example 4: if a is greater than 2 | |
|---|---|
local a = 3
if a > 2 then
print("a = " .. a)
end |
| Example 5: if a less than or equal to 2 | |
|---|---|
local a = 2
if a <= 2 then
print("a = " .. a)
end |
| Example 6: if a less than 2 | |
|---|---|
local a = 0
if a < 2 then
print("a = " .. a)
end |
Mathematical Operators
| + | Add |
| - | Subtract or invert |
| * | Multiply |
| / | Divide |
| ^ | Power |
| % | Remainder |