Difference between revisions of "Dynamic Lighting (h2)"
m |
m |
||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
! style="text-align:left" | Name !! style="text-align:left;width:10%" | By | ! style="text-align:left" | Name !! style="text-align:left;width:10%" | By | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Dynamic Lighting (image based) || AFRLme | + | | Dynamic Lighting (image based) || [https://www.patreon.com/AFRLme AFRLme] |
|} | |} | ||
This tutorial shows you how to create a dynamic light using static images. Dynamic light using images works by creating an image containing the lighting/glow with a transparent background. We then use random values to control the opacity & transition time between current opacity value & the target opacity value. Overall this creates a pretty neat effect. | This tutorial shows you how to create a dynamic light using static images. Dynamic light using images works by creating an image containing the lighting/glow with a transparent background. We then use random values to control the opacity & transition time between current opacity value & the target opacity value. Overall this creates a pretty neat effect. | ||
| + | |||
== Tutorial == | == Tutorial == | ||
| Line 12: | Line 13: | ||
This is the simpler method of the 2 available. It constantly updates the opacity value of the image(s). | This is the simpler method of the 2 available. It constantly updates the opacity value of the image(s). | ||
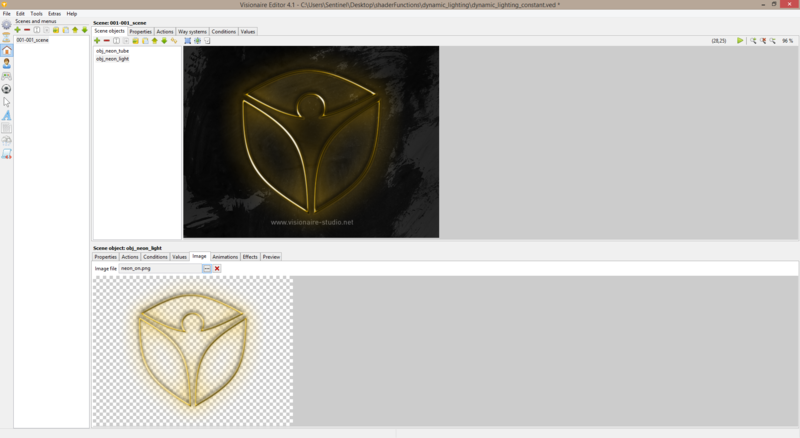
| − | 1. You should create some lighting in your preferred graphic/3D program of choice. | + | 1. You should create some lighting in your preferred graphic/3D program of choice. You need to make sure the edges are smooth, so don't forget to use feather/anti-aliasing etc to create smooth edges for your lighting. Technically you could even create the light image at a smaller scale; say 25% of intended size & then use lua script to scale the image back up to actual size. The lighting layer should have a transparent background. |
| − | 2. First off you are going to want to create an object in your scene that you will be assigning the lighting image to. | + | |
| − | 3. Go to '''scene > | + | [[File:Dyn_light_000.png|800px]] |
| − | 4. Go to: '''scene > actions''' & create | + | |
| − | 5. Inside of the '''at begin of scene''' action: add a ''' | + | 2. First off you are going to want to create an object in your scene that you will be assigning the lighting image to. |
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Dyn_light_001.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
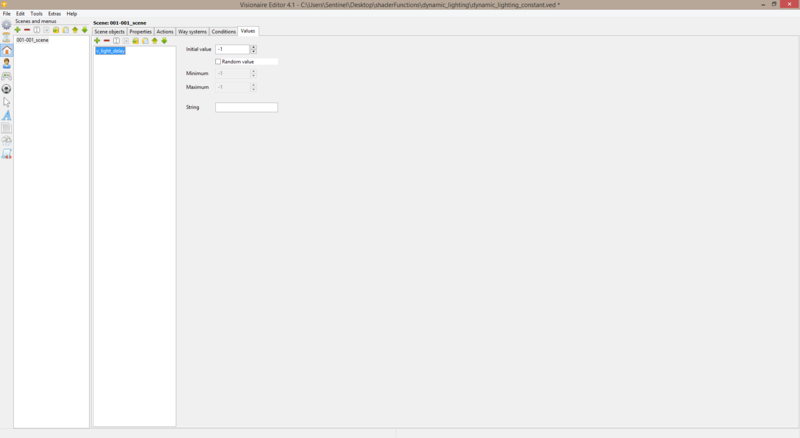
| + | 3. Go to '''scene > values''' & create a new value. This value will be used to control the transition delay. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Dyn_light_002.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
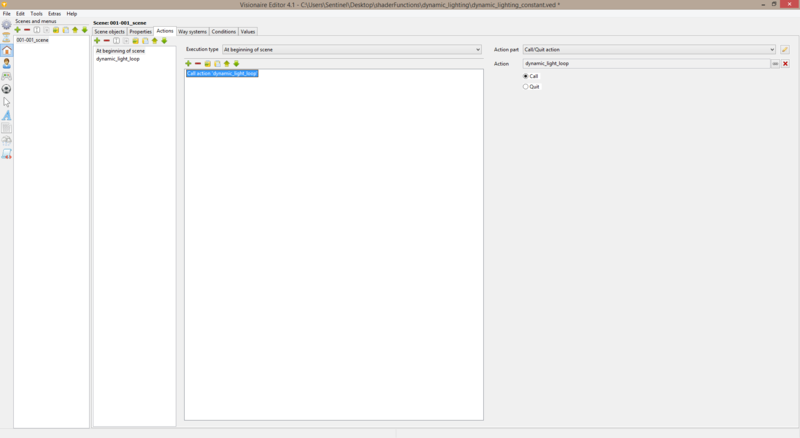
| + | 4. Go to: '''scene > actions''' & create an '''at begin of scene''' action & a '''called by other action''' action. ''Quick note: make sure you give the '''called by other action''' an appropriate name''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 5. Inside of the '''at begin of scene''' action: add a '''call action "called_by_other_action_name"''' action. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Dyn_light_003.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
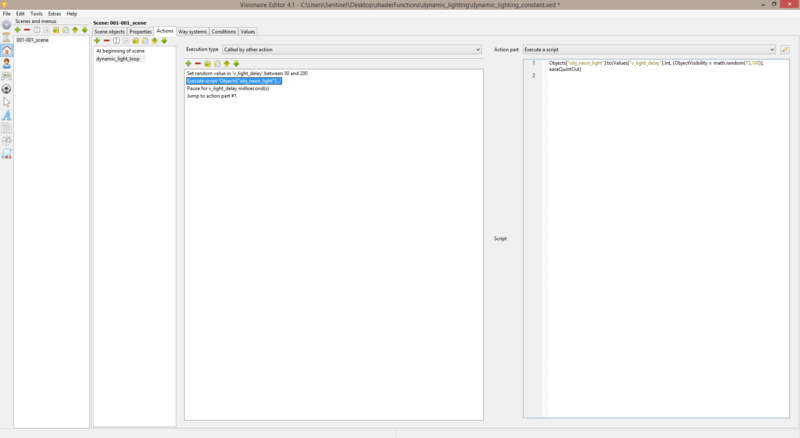
6. Inside of the '''called by other action''' action you should include these action parts... | 6. Inside of the '''called by other action''' action you should include these action parts... | ||
| − | + | set random value in 'value_name' between x and y -- sets random delay between x & y ms. | |
| − | set random value in 'value_name' between | + | execute script > (see code block below) |
| − | execute script > (see code block below) | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> |
| − | + | Objects["object_name"]:to(Values["value_name"].Int, {ObjectVisibility = math.random(75,100)}, easeQuintOut) -- fade to random opacity value between 75-100% with smooth ending | |
| − | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | pause for 'value_name' millisecond(s) -- linked to value. | ||
| + | jump to action part #1 -- forces loop from beginning. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Dyn_light_004.png|800px]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
7. Rinse & repeat the process for other images you want to control with this method. If you don't mind all images being adjusted at the same time, then you could even add them to the '''execute a script''' code mentioned above. | 7. Rinse & repeat the process for other images you want to control with this method. If you don't mind all images being adjusted at the same time, then you could even add them to the '''execute a script''' code mentioned above. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== Flicker === | === Flicker === | ||
This is the more complicated of the 2 methods as it requires additional values, actions & if queries to create the flicker effect. This style of lighting is good for neon lights or in scenarios that require the lighting to flicker on/off. | This is the more complicated of the 2 methods as it requires additional values, actions & if queries to create the flicker effect. This style of lighting is good for neon lights or in scenarios that require the lighting to flicker on/off. | ||
| − | 1. You should create some lighting in your preferred graphic/3D program of choice. | + | 1. You should create some lighting in your preferred graphic/3D program of choice. You need to make sure the edges are smooth, so don't forget to use feather/anti-aliasing etc to create smooth edges for your lighting. Technically you could even create the light image at a smaller scale; say 25% of intended size & then use lua script to scale the image back up to actual size. The lighting layer should have a transparent background. |
| − | 2. First off you are going to want to create an object in your scene that you will be assigning the lighting image to. | + | |
| − | 3. Go to '''scene > | + | [[File:Dyn_light_000.png|800px]] |
| − | 4. Go to: '''scene > actions''' & create | + | |
| − | + | 2. First off you are going to want to create an object in your scene that you will be assigning the lighting image to. | |
| − | set random value in 'value_name' between | + | |
| − | execute script > (see code block below) | + | [[File:Dyn_light_001.png|800px]] |
| − | + | ||
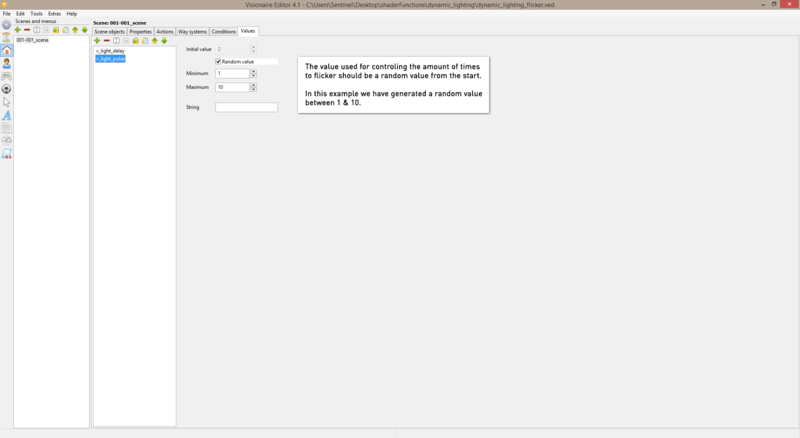
| − | + | 3. Go to '''scene > values''' & create 2 new values. These values will be used to control the transition delay & the amount of times the image should flicker. | |
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Dyn_light_005.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4. Go to: '''scene > actions''' & create an '''at begin of scene''' action & a '''called by other action''' action. ''Quick note: make sure you give the '''called by other action''' an appropriate name''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 5. Inside of the '''at begin of scene''' action: add a '''call action "called_by_other_action_name"''' action (step is optional depending on how light is triggered) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Dyn_light_002.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
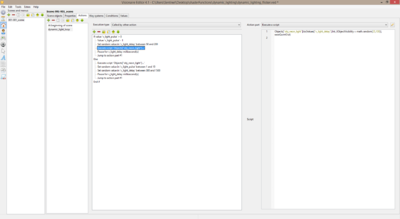
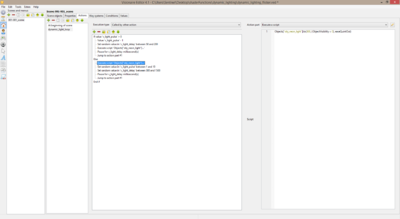
| + | 6. Inside of the '''called by other action''' action you should include these action parts... | ||
| + | |||
| + | if value 'flicker_value_name' > 0 | ||
| + | value 'flicker_value_name' - 1 -- remove 1 from value. | ||
| + | set random value in 'value_name' between x and y -- sets random delay between x & y ms. | ||
| + | execute script > (see code block below) | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> | ||
| + | Objects["object_name"]:to(Values["delay_value_name"].Int, {ObjectVisibility = math.random(25,100)}, easeQuintOut) -- fade to random opacity value between 25-100% with smooth ending | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | pause for 'delay_value_name' millisecond(s) -- linked to delay value. | ||
| + | jump to action part #1 -- forces loop from beginning. | ||
| + | else -- if flicker value = 0 then... | ||
| + | execute a script > (see code block below) | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> | ||
| + | Objects["object_name"]:to(300, {ObjectVisibility = 0}, easeQuintOut) -- fade to 0% opacity over 300ms with smooth ending | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | set random value in 'flicker_value_name' between x & y -- set next random flicker value. | ||
| + | set random value in 'delay_value_name' between x & y -- set random delay value between next set of light flickers. | ||
| + | pause for 'delay_value_name' millisecond(s) -- linked to delay value. | ||
| + | jump to action part #1 -- forces loop from beginning. | ||
| + | end if | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Dyn_light_006.png|400px]] [[File:Dyn_light_007.png|400px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | 7. Rinse & repeat the process for other images you want to control with this method. If you don't mind all images being adjusted at the same time, then you could even add them to the '''execute a script''' code mentioned above. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Resources == | == Resources == | ||
| Line 64: | Line 98: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[media:dynamic_lighting.zip|dynamic_lighting.zip]] || A working .ved file, complete with resources. Check out the readme.txt file for instructions. | | [[media:dynamic_lighting.zip|dynamic_lighting.zip]] || A working .ved file, complete with resources. Check out the readme.txt file for instructions. | ||
| − | |} | + | |}{{toc}} |
| − | {{toc}} | ||
Latest revision as of 21:13, 17 May 2020
| Name | By |
|---|---|
| Dynamic Lighting (image based) | AFRLme |
This tutorial shows you how to create a dynamic light using static images. Dynamic light using images works by creating an image containing the lighting/glow with a transparent background. We then use random values to control the opacity & transition time between current opacity value & the target opacity value. Overall this creates a pretty neat effect.
Tutorial
Constant
This is the simpler method of the 2 available. It constantly updates the opacity value of the image(s).
1. You should create some lighting in your preferred graphic/3D program of choice. You need to make sure the edges are smooth, so don't forget to use feather/anti-aliasing etc to create smooth edges for your lighting. Technically you could even create the light image at a smaller scale; say 25% of intended size & then use lua script to scale the image back up to actual size. The lighting layer should have a transparent background.
2. First off you are going to want to create an object in your scene that you will be assigning the lighting image to.
3. Go to scene > values & create a new value. This value will be used to control the transition delay.
4. Go to: scene > actions & create an at begin of scene action & a called by other action action. Quick note: make sure you give the called by other action an appropriate name.
5. Inside of the at begin of scene action: add a call action "called_by_other_action_name" action.
6. Inside of the called by other action action you should include these action parts...
set random value in 'value_name' between x and y -- sets random delay between x & y ms. execute script > (see code block below)
Objects["object_name"]:to(Values["value_name"].Int, {ObjectVisibility = math.random(75,100)}, easeQuintOut) -- fade to random opacity value between 75-100% with smooth ending
pause for 'value_name' millisecond(s) -- linked to value. jump to action part #1 -- forces loop from beginning.
7. Rinse & repeat the process for other images you want to control with this method. If you don't mind all images being adjusted at the same time, then you could even add them to the execute a script code mentioned above.
Flicker
This is the more complicated of the 2 methods as it requires additional values, actions & if queries to create the flicker effect. This style of lighting is good for neon lights or in scenarios that require the lighting to flicker on/off.
1. You should create some lighting in your preferred graphic/3D program of choice. You need to make sure the edges are smooth, so don't forget to use feather/anti-aliasing etc to create smooth edges for your lighting. Technically you could even create the light image at a smaller scale; say 25% of intended size & then use lua script to scale the image back up to actual size. The lighting layer should have a transparent background.
2. First off you are going to want to create an object in your scene that you will be assigning the lighting image to.
3. Go to scene > values & create 2 new values. These values will be used to control the transition delay & the amount of times the image should flicker.
4. Go to: scene > actions & create an at begin of scene action & a called by other action action. Quick note: make sure you give the called by other action an appropriate name.
5. Inside of the at begin of scene action: add a call action "called_by_other_action_name" action (step is optional depending on how light is triggered)
6. Inside of the called by other action action you should include these action parts...
if value 'flicker_value_name' > 0 value 'flicker_value_name' - 1 -- remove 1 from value. set random value in 'value_name' between x and y -- sets random delay between x & y ms. execute script > (see code block below)
Objects["object_name"]:to(Values["delay_value_name"].Int, {ObjectVisibility = math.random(25,100)}, easeQuintOut) -- fade to random opacity value between 25-100% with smooth ending
pause for 'delay_value_name' millisecond(s) -- linked to delay value. jump to action part #1 -- forces loop from beginning. else -- if flicker value = 0 then... execute a script > (see code block below)
Objects["object_name"]:to(300, {ObjectVisibility = 0}, easeQuintOut) -- fade to 0% opacity over 300ms with smooth ending
set random value in 'flicker_value_name' between x & y -- set next random flicker value. set random value in 'delay_value_name' between x & y -- set random delay value between next set of light flickers. pause for 'delay_value_name' millisecond(s) -- linked to delay value. jump to action part #1 -- forces loop from beginning. end if
7. Rinse & repeat the process for other images you want to control with this method. If you don't mind all images being adjusted at the same time, then you could even add them to the execute a script code mentioned above.
Resources
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| dynamic_lighting.zip | A working .ved file, complete with resources. Check out the readme.txt file for instructions. |