Difference between revisions of "Basic Lua: Operators"
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
== Conditional Operators == | == Conditional Operators == | ||
{| class="ts" | {| class="ts" | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | [[Basic_lua:_Operators#if|if]] || Query if something does or does not meet a certain condition. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | [[Basic_lua:_Operators#else|else]] || Do something else if the query condition was not met. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | end | + | | [[Basic_lua:_Operators#elseif|elseif]] || Used to add additional if queries, if the initial query condition was not met. |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Basic_lua:_Operators#end|end]] || This is used to close various queries or functions; there must be the same amount of '''end''' as '''if'''; except in instances where '''elseif''' has been used. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
=== if === | === if === | ||
Revision as of 22:04, 2 November 2018
Lua operators are expressions used to perform calculations or to pass arguments between different value types.
| < | Index | > |
Conditional Operators
| if | Query if something does or does not meet a certain condition. |
| else | Do something else if the query condition was not met. |
| elseif | Used to add additional if queries, if the initial query condition was not met. |
| end | This is used to close various queries or functions; there must be the same amount of end as if; except in instances where elseif has been used. |
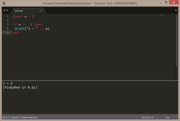
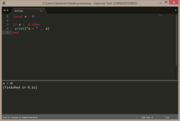
if
if statements are one of the most common staples of programming, because programs & games & just about everything we do in life consists of if queries; should I wear this tie today? Do I need to go grocery shopping after work? Should I buy this game, or that game? etc. etc.
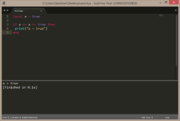
Let's say that we have a variable called var & we want to check if the var contains a boolean value of true...
local var = true
if var == true then
print("var = true")
end
| Quick note: if a variable contains a boolean value of true or false, then there is no need to use definitive query based operators as the variable on it's own will return the boolean value. |
Now we want to perform the same query, but we want to check if the variable is false instead...
local var = true
if var == false then
print("var = false")
end
What do you think will happen when we run the code above? That's right, absolutely nothing will happen because var still contains the boolean value of true & we haven't told the program what to do if the variable doesn't return false, so let's do that now by using an else operator...
else
local var = true
if var == false then
print("var = false")
else
print("var = true")
end
Because the variable contains a boolean value of true, we skip the if var == false block of code & execute the line of code in the else section instead, which would print "var = true" to the log.
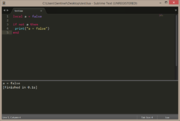
elseif
| if condition is not met, then do else | |
|---|---|
local a = false
if a then
print("a = true")
else
print("a = false")
end
|
Logical Operators
| and | Allows you to check multiple conditions in a single if query. |
| or | Allows you to add an alternative if query into a single if query. |
| not | Checks if condition equals false or negative. |
and
| if condition a is true and condition b is false then | |
|---|---|
local a = true
local b = false
if a == true and b == false then
print("a = true", "b = false")
end
|
or
| if condition is true or condition == true then | |
|---|---|
local a = true
if a or a == true then
print("a = true")
end |
not
| if condition is not true | |
|---|---|
local a = false
if not a then
print("a = false")
end |
Comparison Operators
| == | Equal to. |
| ~= | Does not equal. |
| >= | Greater than or equal to. |
| > | Greater than. |
| <= | Less than or equal to. |
| < | Less than. |
equal to
| if a equals 1 | |
|---|---|
local a = 1
if a == 1 then
print("a = 1")
end |
does not equal
| if a does not equal 2 | |
|---|---|
local a = 1
if a ~= 2 then
print("a = " .. a)
end |
greater than or equal to
| if a is greater than or equal to 2 | |
|---|---|
local a = 5
if a >= 2 then
print("a = " .. a)
end |
greater than
| if a is greater than 2 | |
|---|---|
local a = 3
if a > 2 then
print("a = " .. a)
end |
less than or equal to
| if a less than or equal to 2 | |
|---|---|
local a = 2
if a <= 2 then
print("a = " .. a)
end |
less than
| if a less than 2 | |
|---|---|
local a = 0
if a < 2 then
print("a = " .. a)
end |
Mathematical Operators
| + | Add |
| - | Subtract or invert |
| * | Multiply |
| / | Divide |
| ^ | Power |
| % | Remainder |
add
| 1 + 2 = 3 | |
|---|---|
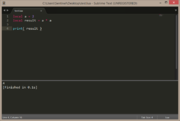
local a = 1
local b = 2
local result = a + b
print( result ) |
subtract
| 3 - 2 = 1 | |
|---|---|
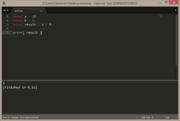
local a = 3
local b = 2
local result = a - b
print( result ) |
inverse
| inv of 3 = -3 | |
|---|---|
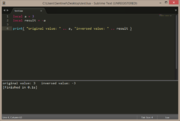
local a = 3
local result = -a
print( "original value: " .. a, "inversed value: " .. result ) |
multiply
| 2 x 2 = 4 | |
|---|---|
local a = 2
local result = a * a
print( result ) |
divide
| 10 ÷ 5 = 2 | |
|---|---|
local a = 10
local b = 5
local result = a / b
print( result ) |
power
| base of 2, power of 8 (2ⁿ) = 256 | |
|---|---|
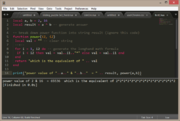
local a, b = 2, 16
local result = a ^ b -- generate answer
-- break down power function into string result (ignore this code)
function power(i1, i2)
local val = "" -- clear string
--+--
for i = 1, i2 do -- generate the longhand math formula
if i < i2 then val = val..i1.."*" else val = val..i1 end
end
return "which is the equivalent of " .. val
end
print("power value of "..a.." & "..b.." = " .. result, power(a,b)) |
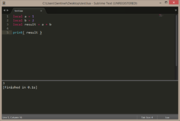
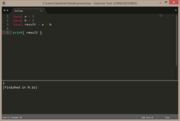
remainder
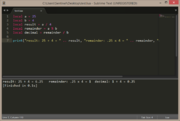
| remainder of 25 ÷ 4 = 1 | |
|---|---|
local a = 25
local b = 4
local result = a / 4
local remainder = a % b
local decimal = remainder / b
print("result: 25 ÷ 4 = " .. result, "remainder: .25 x 4 = " .. remainder, "decimal: 1 ÷ 4 = " .. decimal ) |
| < | Index | > |