Difference between revisions of "Basic lua: Types"
From The Official Visionaire Studio: Adventure Game Engine Wiki
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
{| class="ts" | {| class="ts" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! Example 3: | + | ! Example 3: nil !! |
|- | |- | ||
| <syntaxhighlight> | | <syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | a = nil | |
| − | + | print( a, " type = " .. type(a) ) | |
| − | + | print( b, " type = " .. type(b) ) | |
| − | + | </syntaxhighlight> || width="200px" | [[File:lb_types_003.png|thumb|right|180px|click to enlarge]] | |
| − | </syntaxhighlight> || width="200px" | [[File: | + | |} |
| + | |||
| + | {| class="ts" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Example 4: number !! | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | local a = 7 | ||
| + | |||
| + | print(a, type(a) ) | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> || width="200px" | [[File:lb_types_004.png|thumb|right|180px|click to enlarge]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 17:29, 25 August 2014
There are multiple lua types available, which are automatically determined by the returned value of the variable, function or table.
| < | Index | > |
Conditional Operators
| boolean | This returns a value of true or false. |
| function | A function usually contains a list of actions to be executed & can often be used to calculate & return values. |
| nil | If no data type is returned then whatever you queried is either empty or does not exist, thus it is nil. |
| number | This usually contains an integer (whole) or floating point (decimal) number. |
| string | This usually contains text or numbers wrapped in "quotation marks" or 'apostrophes'. |
| table | This usually consists of an array, or multiple arrays of data & data types. |
| threads | - |
| userdata | - |
| Example 1: boolean | |
|---|---|
local a = true
print( a, type(a) ) |
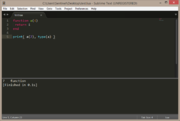
| Example 2: function | |
|---|---|
function a(i)
return i
end
print( a(7), type(a) ) |
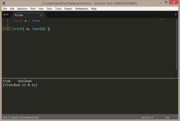
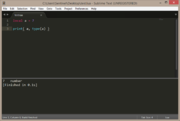
| Example 3: nil | |
|---|---|
a = nil
print( a, " type = " .. type(a) )
print( b, " type = " .. type(b) ) |
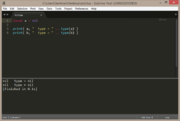
| Example 4: number | |
|---|---|
local a = 7
print(a, type(a) ) |
| < | Index | > |