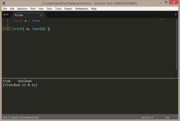
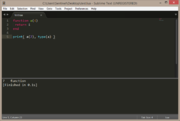
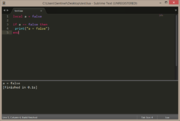
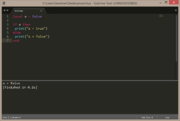
There are multiple lua types available, which are automatically determined by the returned value of the variable, function or table.
Conditional Operators
| boolean |
This returns a value of true or false.
|
| function |
A function usually contains a list of actions to be executed & can often be used to calculate & return values.
|
| nil |
If no data type is returned then whatever you queried is either empty or does not exist, thus it is nil.
|
| number |
This usually contains an integer (whole) or floating point (decimal) number.
|
| string |
This usually contains text or numbers wrapped in "quotation marks" or 'apostrophes'.
|
| table |
This usually consists of an array, or multiple arrays of data & data types.
|
| threads |
-
|
| userdata |
-
|
| Example 1: boolean |
|
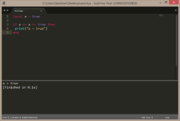
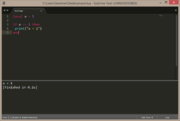
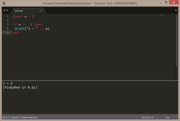
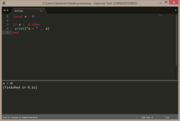
local a = true
print( a, type(a) ) |
|
| Example 2: function |
|
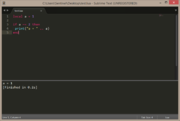
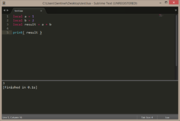
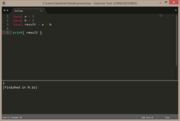
function a(i)
return i
end
print( a(7), type(a) ) |
|
| Example 3: if condition is false |
|
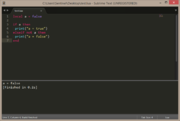
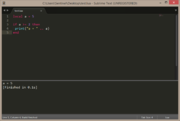
local a = false
if a == false then
print("a = false")
end |
|
| Example 4: if condition is not met, then do else |
|
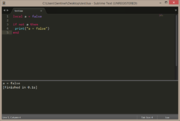
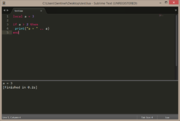
local a = false
if a then
print("a = true")
else
print("a = false")
end |
|
| Example 5: if condition is not met, then do elseif |
|
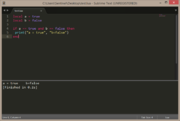
local a = false
if a then
print("a = true")
elseif not a then
print("a = false")
end |
|
Logical Operators
| and |
Allows you to check multiple conditions in a single if query.
|
| or |
Allows you to add an alternative if query into a single if query.
|
| not |
Checks if condition equals false or negative.
|
| Example 1: if condition a is true and condition b is false then |
|
local a = true
local b = false
if a == true and b == false then
print("a = true", "b=false")
end |
|
| Example 2: if condition is true or condition == true then |
|
local a = true
if a or a == true then
print("a = true")
end |
|
| Example 3: if condition is not true |
|
local a = false
if not a then
print("a = false")
end |
|
Comparison Operators
| == |
Equal to.
|
| ~= |
Does not equal.
|
| >= |
Greater than or equal to.
|
| > |
Greater than.
|
| <= |
Less than or equal to.
|
| < |
Less than.
|
| Example 1: if a equals 1 |
|
local a = 1
if a == 1 then
print("a = 1")
end |
|
| Example 2: if a does not equal 2 |
|
local a = 1
if a ~= 2 then
print("a = " .. a)
end |
|
| Example 3: if a is greater than or equal to 2 |
|
local a = 5
if a >= 2 then
print("a = " .. a)
end |
|
| Example 4: if a is greater than 2 |
|
local a = 3
if a > 2 then
print("a = " .. a)
end |
|
| Example 5: if a less than or equal to 2 |
|
local a = 2
if a <= 2 then
print("a = " .. a)
end |
|
| Example 6: if a less than 2 |
|
local a = 0
if a < 2 then
print("a = " .. a)
end |
|
Mathematical Operators
| + |
Add
|
| - |
Subtract or invert
|
| * |
Multiply
|
| / |
Divide
|
| ^ |
Power
|
| % |
Remainder
|
| Example 1: 1 +2 = 3 |
|
local a = 1
local b = 2
local result = a + b
print( result ) |
|
| Example 2: 3 - 2 = 1 |
|
local a = 3
local b = 2
local result = a - b
print( result ) |
|
| Example 3: inversed values |
|
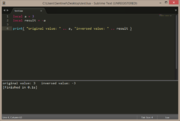
local a = 3
local result = -a
print( "original value: " .. a, "inversed value: " .. result ) |
|
| Example 4: 2 x 2 = 4 |
|
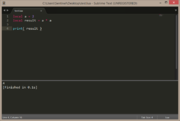
local a = 2
local result = a * a
print( result ) |
|
| Example 5: 10 ÷ 5 = 2 |
|
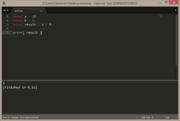
local a = 10
local b = 5
local result = a / b
print( result ) |
|
| Example 6: base of 2, power of 8 (2ⁿ) = 256 |
|
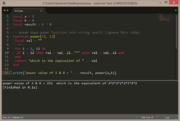
local a = 2
local b = 8
local result = 2 ^ 8
-- break down power function into string result (ignore this code)
function power(i1, i2)
local val = ""
--+--
for i = 1, i2 do
if i < i2 then val = val..i1.."*" else val = val..i1 end
end
return "which is the equivalent of " .. val
end
print("power value of 2 & 8 = " .. result, power(a,b)) |
|
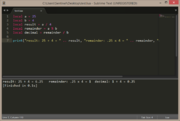
| Example 7: remainder of 25 ÷ 4 = 1 |
|
local a = 25
local b = 4
local result = a / 4
local remainder = a % b
local decimal = remainder / b
print("result: 25 ÷ 4 = " .. result, "remainder: .25 x 4 = " .. remainder, "decimal: 1 ÷ 4 = " .. decimal ) |
|